Sas Functions Cheat Sheet
I have created this SAS cheat sheet to refer while you learn. It has all the important procedures and functions which come very handy.
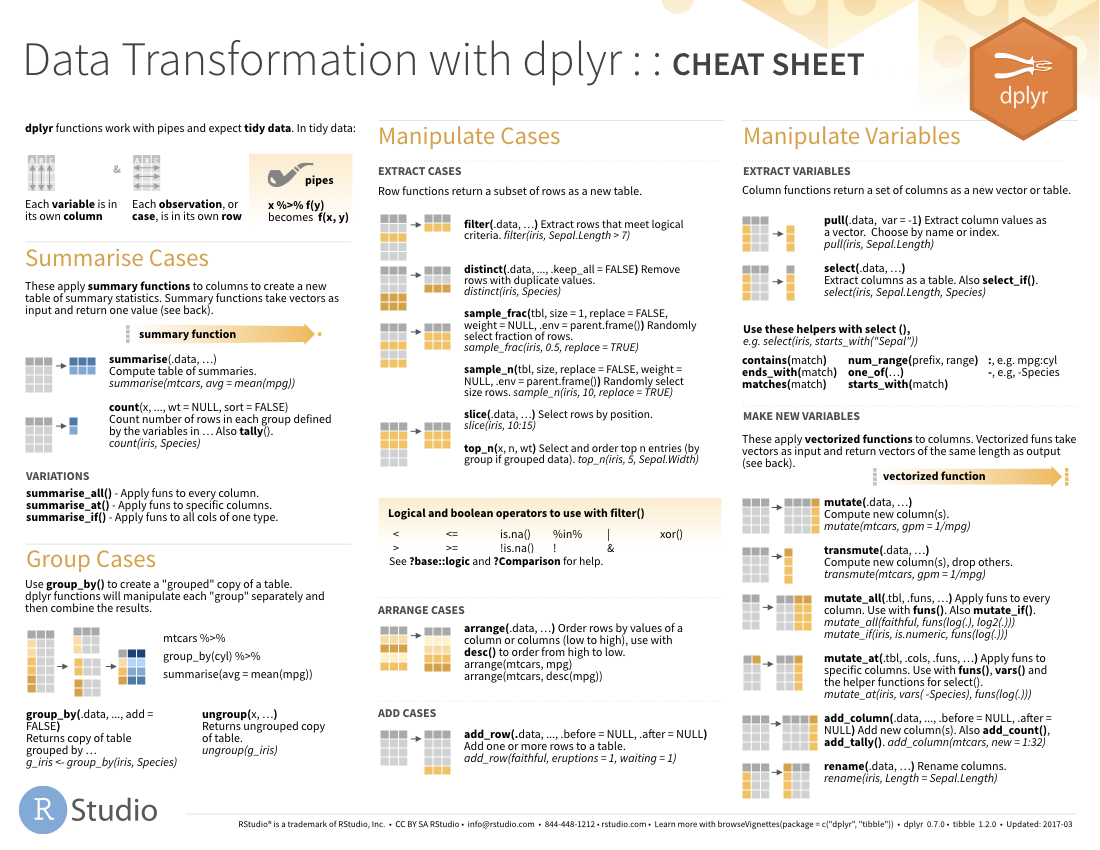
Sas cheat sheet 1. Modifying data- numerical changes 1. Structure of the data data libname.newdata; proc contents libname.dataset. String functions proc print.
SAS Language
Get the Sas Cheat Sheet you require. Open it up using the cloud-based editor and begin adjusting. Fill the blank fields; involved parties names, addresses and numbers etc. Customize the blanks with smart fillable areas. Include the day/time and place your electronic signature. Simply click Done after twice-examining everything. Cheat Sheet: The pandas DataFrame Object by Mark Graph and located at the University of Idaho’s web-site. Working with missing data pandas 0.19.1 documentation. This post is an excerpt from Randy Betancourt Python for SAS Users quick start guide. View the full Chapter List.
ATTRIBvarn <LENGTH=’varn-length’> <LABEL=’varn-label’>
<FORMAT=varn-format.> <INFORMAT=varn-informat.>;
Associates a format, informat, label, and/or length with one
or more variables
CARDS or CARDS4 | DATALINES or DATALINES4
Indicates that data lines follow (suffix of 4 if data has ‘;’s).
DATA <dsetn <(dset-optionsn)>>;
Begins a DATA step and provides names for any output
SAS data sets. See Data Set Options for options that are

available in the DATA statement.
DO index-var=start_valueTOend_value <BYstep>;
DO UNTIL (expression);
DO WHILE (expression);
Groups a set of statements as a single unit. Note that UNTIL conditions are evaluated at the end of the loop and
thus execute at least once.
FILE filename <options>;
Specifies the current output file for PUT statements. Options include:
MOD output is appended to an existing file.
OLD output overwrites an existing file.
IF expressionTHENstatement; …. <ELSE> statement;
SAS evaluates the expression in an IF statement to
produce a result that is either non-zero, zero, or missing. If
result >0 then TRUE, else FALSE.
INFILE filename <options>;
Specifies an external file to read with an INPUT statement. Options include:
DELIMITER|DLM= delimiters
Specifies a delimiter for list input. LENGTH= variable
Names a variable that SAS sets to the length of the
current input line.
INPUTvar<=> <$> startcol <-endcol> <.dec> <@ | @@>; INPUT <pointer-control> variable informat. <@ | @@>;INPUT<pointer-control> variable <$> <&> <@ | @@>;
Input records from the current input file, placing the values
into SAS variables.
MERGE ds1 <(doptions)> <… dsn<(doptions)>> <END=var>;
Joins observations from two or more SAS data sets into
single observations.
OUTPUT<data-set-name(s)>;
Writes the current observation to a SAS data set.
PUTvar<=> <$> startcol <-endcol> <.dec> <@ | @@>;
PUT <pointer-control> <”text”|variable format.> <@ | @@>;
Writes variable values and/or text to the output line.
RETAINvariablen <initial-valuen>;
Causes a variable to retain its value from one iteration of
the data step to the next.
SET<data-set(s) <(data-set-options(s)>> <POINT=varname>
<NOBS=varname> <END=varname>;
Reads observations from one or more data sets.
—————————————————————————————————————————————

SAS Data Set Options
DROP=variable(s) Excludes variables from processing. FIRSTOBS=n Specifies the first observation to process IN=variable Creates and names a variable that indicates
whether the data set contributed data to the current
observation.
KEEP=variable(s) Selects variables for processing. LABEL=’label‘ Specifies a label for a SAS data set
OBS=n Specifies the first n observations to process POINT=variable Direct observation number variable

RENAME=(oldname1=newname1 <…oldnamen=newnamen>)
Changes the name of a variable.
WHERE=(expression1 <logical-operator expressionn>)
Selects observations from a SAS data set that meet certain conditions before SAS brings them into the DATA or PROC step for processing.
——————————————————————————————————————————————
SAS Procedures
PROC COMPARE <BASE=dset> <COMPARE=dset>;
BYvariable(s);

IDvariable(s);
VAR variable(s);
PROC DATASETS <LIBRARY=libref> <MEMTYPE=(m-list)>
<DETAILS|NODETAILS> <KILL>
<NOLIST>;
APPEND BASE=dset <DATA=dset> <FORCE>;
CHANGEold-namen=new-namen </MEMTYPE=(m-list);
Sas Hash Cheat Sheet
CONTENTS <DATA=<libref.>member> <DIRECTORY>
<MEMTYPE=(m-list)> <NODS>
<VARNUM> <NOPRINT> <OUT=dset>;
COPY OUT=libref <IN=libref> <MEMTYPE=(m-list)>
<MOVE>;
EXCLUDEmember-list </MEMTYPE=mtype>;
LABEL variable=’label-text’;
RENAME variablen=new-variablen;
QUIT;
where
m-list one or more of the member types that processing should be restricted to.
member-list list of members in the directory to process.
PROC EXPORT DATA=<libref.>dset
OUTFILE=”filename” <REPLACE>;
PROC IMPORT DATAFILE=”filename”
OUT=<libref.>dset <REPLACE>;
The following filetypes are the most commonly used and supported within filename by SAS:
Sas Cheat Sheet Pdf
filename.XLS (Microsoft Excel)
filename.TXT (tab delimited)
Sas Functions Cheat Sheet Examples
filename.CSV (comma separated value)
